Finite element program for solid mechanics
This program solves the 2d plate stress problem for the classical problem of a hole in a plate. This program was used for a study on the stress generated by two adjacent holes. More information on the program and FEA is given in one of my whitepapers. The case of a hole in a plate was used for validating the code. If the hole diameter is small enough compared to the length of the plate, the stresses produced around a hole in a loaded plate will be close to the ones produced if the plate was infinite in size. The analytical solution for the stress tangent to the edge of the hole in an infinite plate is known and is given by:
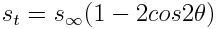
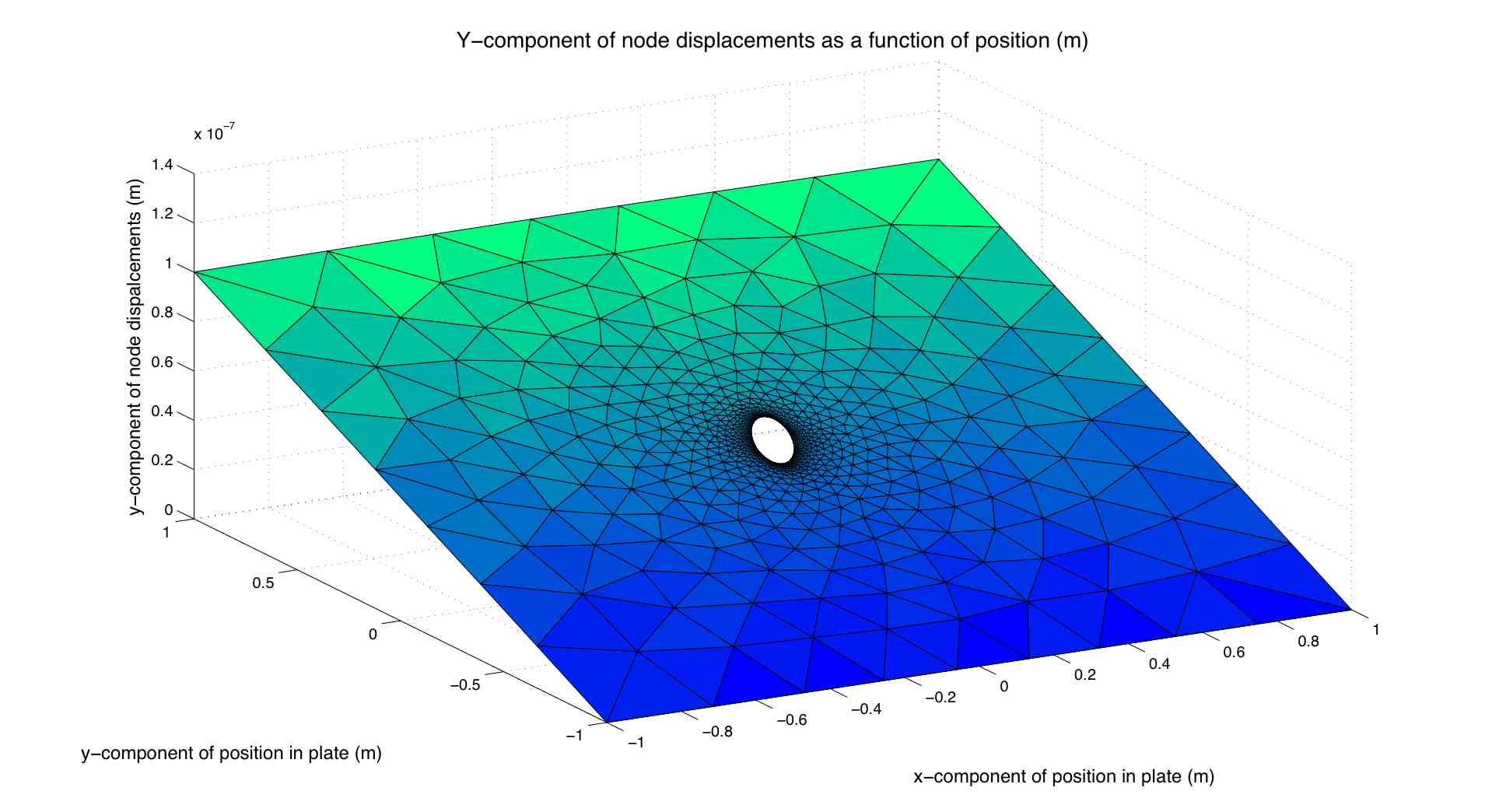
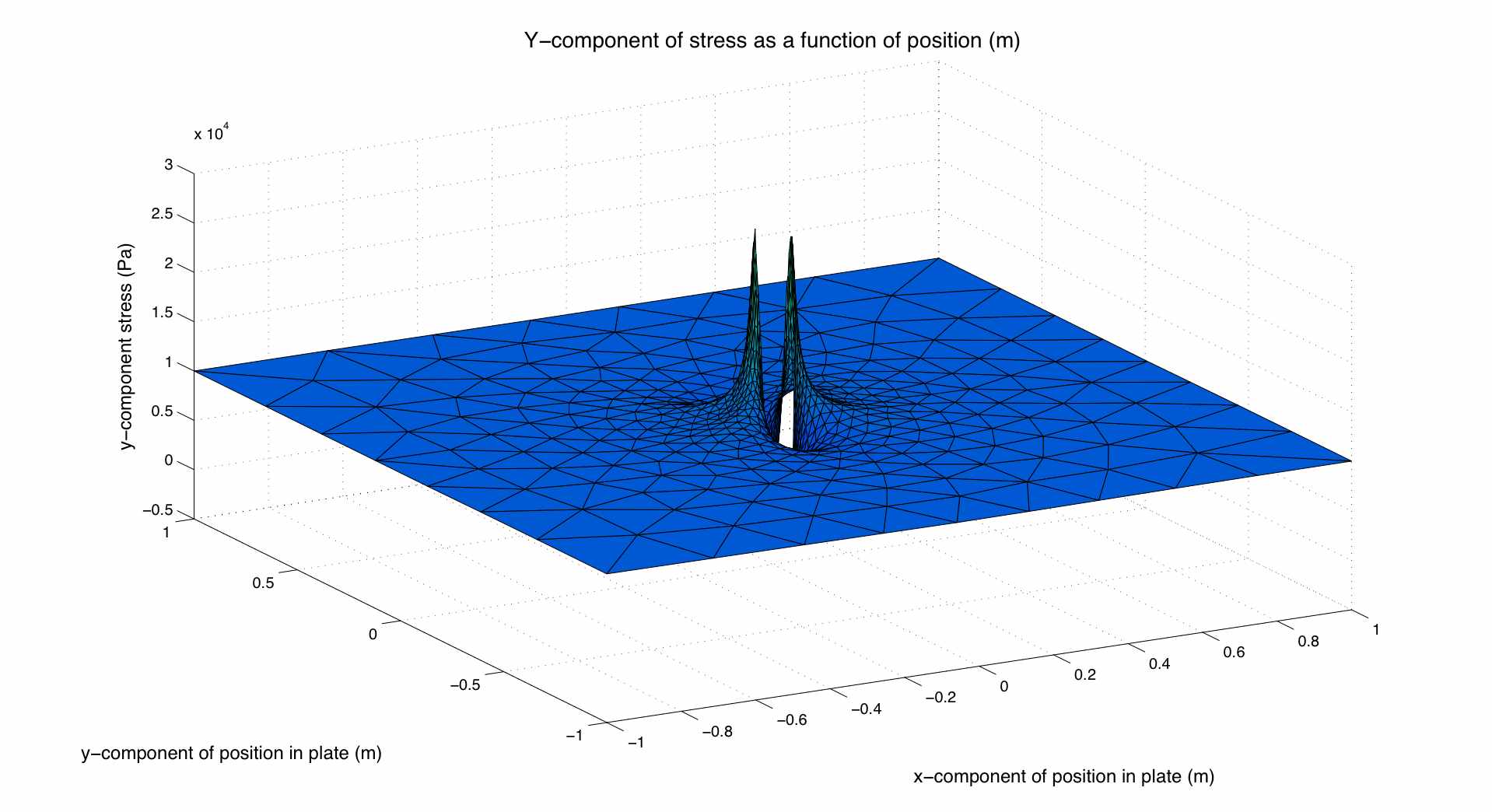
Where s at infinity is the applied stress on the plate and theta is measured from the loading axis at the center of the hole. This closely matches the output given by the program. The program uses an excellent mesh generator called distmesh and its based on the code given in this paper. Information on how to calculate the stress form the displacements is hard to come by, even online. The best website I have found on the practical issues of finite element analysis (FEA) programming is this one. It has a good section on computing the stresses from the computed displacements which is called: Stress recovery. As seen from the nodal displacements, the displacement is constant at the loaded edge of the plate, also indicating that the infinite hole in a plate solution applies to the geometric properties used in the program. For better results (same result with less elements), a quadrilateral mesh should be used since linear triangular elements have constant strain.
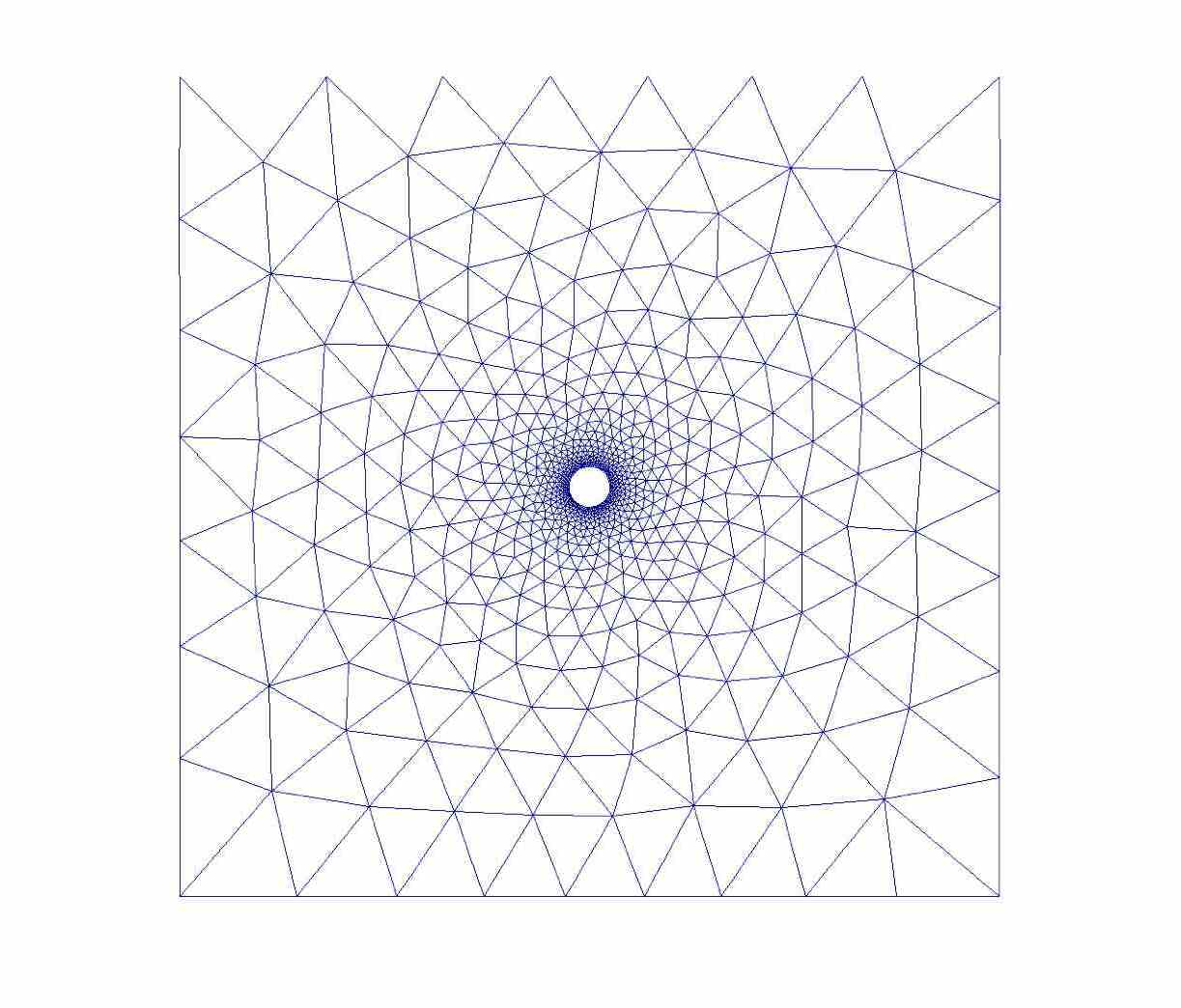
The mesh generated by distmesh and its close-up are shown below:
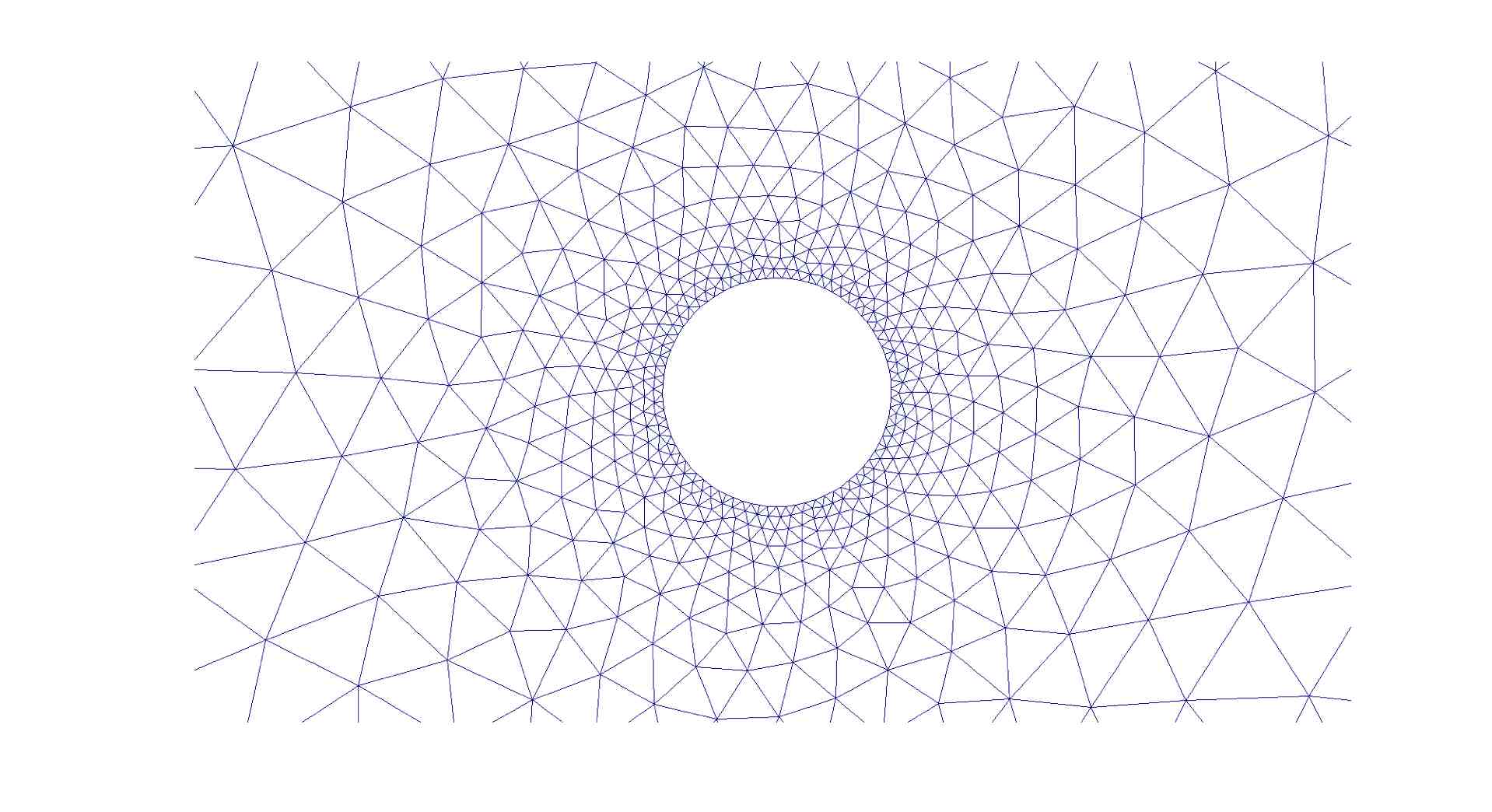
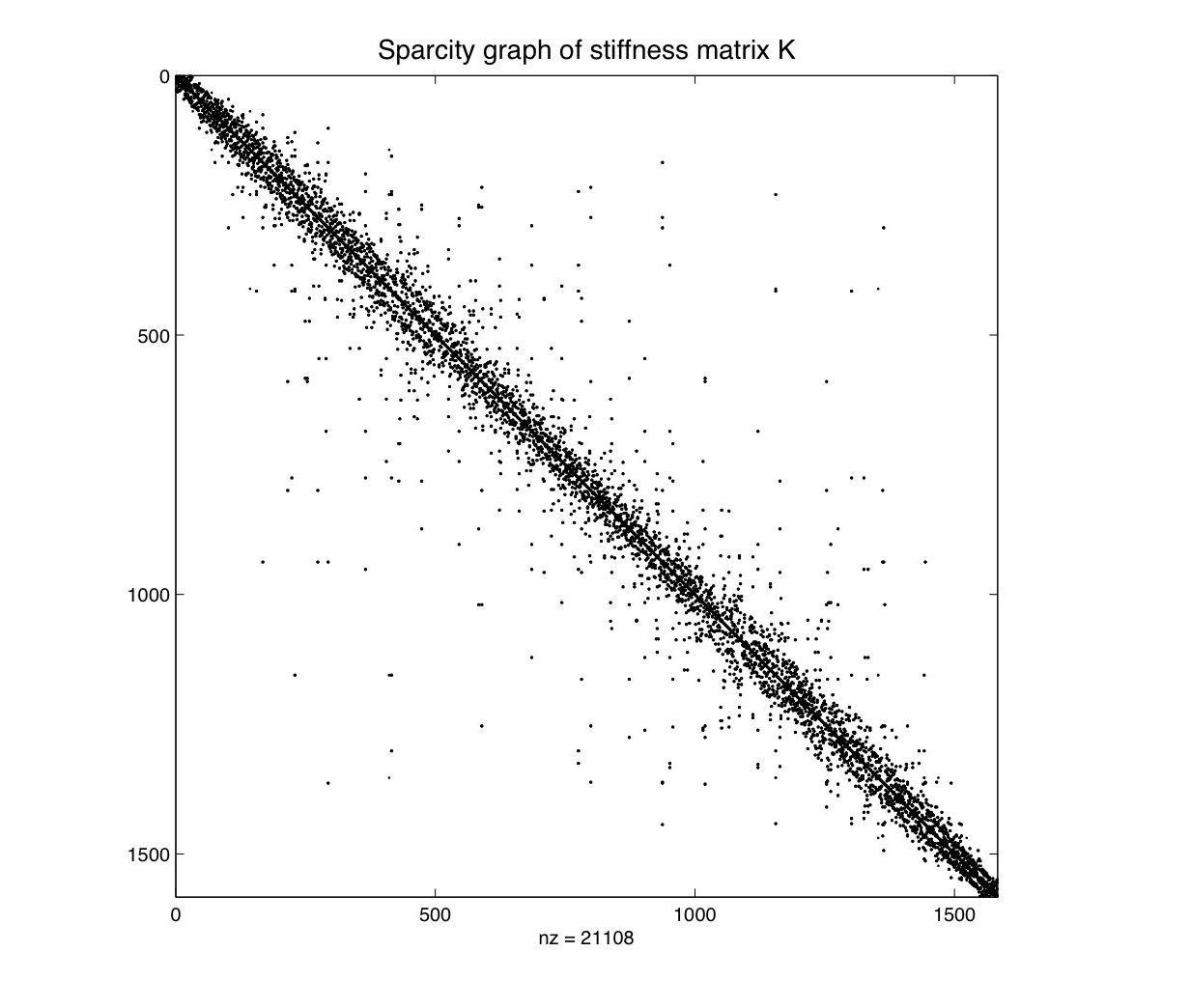
The plot below shows the sparsity graph (plot) of the stiffness matrix:
The plots below show the computed displacement and the stress in the y direction: